As you consider starting your investment journey, you’re likely filled with a mix of excitement and uncertainty. Investing can seem daunting, especially with the numerous options and complexities involved. However, with the right approach and knowledge, you can set yourself up for long-term financial success. In this article, you’ll learn the fundamentals of investing, how to set financial goals, and the steps to create a personalized investment plan. By the end of this journey, you’ll be equipped with the insights and confidence to make informed investment decisions and start building your wealth.
You’ll discover how to avoid common pitfalls, such as investing without a clear strategy or failing to diversify your portfolio. You’ll also learn about the various investment options available, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, and how to choose the ones that align with your goals and risk tolerance. Whether you’re looking to save for a down payment on a house, retirement, or a big purchase, the principles outlined in this article will provide you with a solid foundation to achieve your financial objectives.
Introduction to Investing
Investing is the act of allocating your money into assets that have a potential for growth, income, or both. It involves putting your money into various financial instruments, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, with the expectation of earning a return on your investment. Investing can help you achieve your long-term financial goals, such as retirement, buying a house, or funding your children’s education. The benefits of investing are numerous, including the potential for higher returns than traditional savings accounts, tax advantages, and the ability to build wealth over time.
For example, consider the story of Warren Buffett, one of the most successful investors in history. Buffett started investing at a young age and has consistently demonstrated the power of long-term investing. By investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks and businesses, Buffett has built a net worth of over $100 billion. His success is a testament to the potential of investing and the importance of starting early.
When it comes to investing, it’s essential to understand the concept of compound interest. Compound interest is the interest earned on both the principal amount and any accrued interest over time. This means that your investments can grow exponentially, providing a significant return on your investment. For instance, if you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 5%, you’ll earn $50 in interest in the first year, making your total investment worth $1,050. In the second year, you’ll earn 5% interest on the new total of $1,050, resulting in $52.50 in interest, and so on.
Setting Financial Goals

Short-Term Goals
Short-term goals are typically those that you want to achieve within the next five years. These goals may include saving for a down payment on a house, paying off high-interest debt, or building an emergency fund. When setting short-term goals, it’s essential to be specific, measurable, and realistic. For example, instead of saying “I want to save money,” you could say “I want to save $10,000 for a down payment on a house within the next two years.”
To achieve your short-term goals, you’ll need to create a budget and track your expenses. This will help you understand where your money is going and identify areas where you can cut back. You can use the 50/30/20 rule as a guideline, allocating 50% of your income towards necessary expenses, 30% towards discretionary spending, and 20% towards saving and debt repayment.
Long-Term Goals
Long-term goals are those that you want to achieve over a period of five years or more. These goals may include retirement, funding your children’s education, or buying a vacation home. When setting long-term goals, it’s essential to consider your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and expected returns. For example, if you’re saving for retirement, you may want to consider investing in a tax-advantaged retirement account, such as a 401(k) or IRA.
A good example of a long-term goal is saving for retirement. Let’s say you’re 30 years old and want to retire at 65. You can use a retirement calculator to determine how much you need to save each month to reach your goal. Assuming you want to retire with a nest egg of $1 million, and you expect to earn an average annual return of 7% on your investments, you may need to save around $500 per month for the next 35 years.
Understanding Investment Options
There are numerous investment options available, each with its own unique characteristics, benefits, and risks. Stocks, also known as equities, represent ownership in companies. They offer the potential for long-term growth, but come with higher volatility and risk. Bonds, on the other hand, represent debt obligations issued by companies or governments. They offer regular income and relatively lower risk, but may not keep pace with inflation.
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They offer professional management, diversification, and economies of scale, but may come with higher fees and expenses. Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are similar to mutual funds but trade on an exchange like stocks, offering flexibility and transparency.
For example, consider the S&P 500 index fund, which tracks the performance of the 500 largest publicly traded companies in the US. This fund offers broad diversification, low costs, and the potential for long-term growth. Alternatively, you could consider investing in sector-specific ETFs, such as a technology or healthcare ETF, to gain exposure to specific industries or sectors.
When evaluating investment options, it’s essential to consider your investment horizon, risk tolerance, and financial goals. You should also evaluate the fees and expenses associated with each investment, as well as the tax implications. By doing your research and seeking professional advice, you can create a well-diversified portfolio that aligns with your needs and objectives.
Creating an Investment Plan
Creating an investment plan involves assessing your financial situation, setting clear goals, and selecting the right investment vehicles. It’s essential to assess your risk tolerance, which refers to your ability to withstand market fluctuations and potential losses. You should also evaluate your investment horizon, which is the time period you have to achieve your financial goals.
A well-diversified investment portfolio is critical to achieving your financial goals. This involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to minimize risk and maximize returns. You can use asset allocation models to determine the optimal mix of assets for your portfolio, based on your risk tolerance and investment horizon.
For example, a conservative investor may allocate 40% of their portfolio to stocks, 30% to bonds, and 30% to cash and cash equivalents. A moderate investor may allocate 60% to stocks, 20% to bonds, and 20% to cash and cash equivalents. A aggressive investor may allocate 80% to stocks, 10% to bonds, and 10% to cash and cash equivalents.
When creating an investment plan, it’s also essential to consider tax implications and fees and expenses. You should aim to minimize taxes and fees, while maximizing your returns. You can use tax-advantaged accounts, such as 401(k) or IRA, to reduce your tax liability and optimize your investment returns.
Managing Risk and Diversification
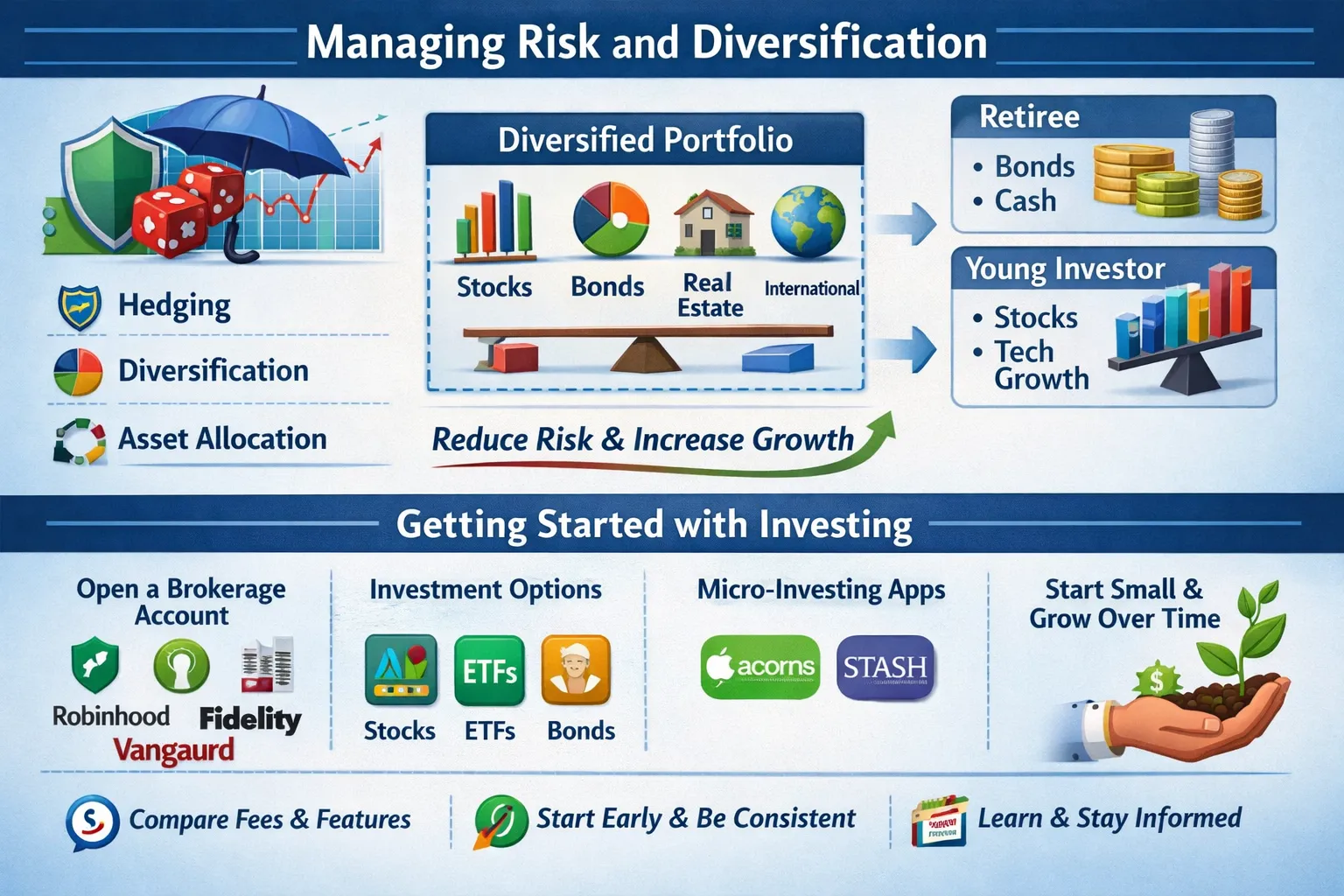
Managing risk is a critical aspect of investing. It involves identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, and implementing strategies to mitigate them. Diversification is a key risk management strategy, which involves spreading your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies to minimize risk.
There are several risk management strategies you can use, including hedging, diversification, and asset allocation. Hedging involves taking a position in a security that offsets the risk of another investment. Diversification, as mentioned earlier, involves spreading your investments across different asset classes and sectors. Asset allocation involves allocating your investments across different asset classes, based on your risk tolerance and investment horizon.
For example, consider the portfolio of a retiree, which may be heavily weighted towards bonds and cash equivalents to minimize risk. In contrast, the portfolio of a young investor may be more aggressive, with a higher allocation to stocks and other growth-oriented investments. By diversifying your portfolio and managing risk, you can reduce the potential for losses and increase the potential for long-term growth.
It’s also essential to monitor and adjust your investment portfolio regularly. This involves reviewing your investments, assessing their performance, and making adjustments as needed. You should also rebalance your portfolio periodically, to ensure that it remains aligned with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Getting Started with Investing
Getting started with investing can seem daunting, but it’s easier than you think. You can start by opening a brokerage account, which will give you access to a range of investment products and services. You can choose from a variety of investment apps, such as Robinhood, Fidelity, or Vanguard, which offer low-cost trading, research tools, and educational resources.
When selecting a brokerage account, consider fees and commissions, investment options, and customer support. You should also evaluate the user experience and mobile accessibility of the platform. For example, some investment apps offer robo-advisory services, which provide automated investment management and portfolio rebalancing.
Once you’ve opened a brokerage account, you can start investing in a range of assets, including stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds. You can also consider micro-investing apps, which allow you to invest small amounts of money into a diversified portfolio. For example, apps like Acorns or Stash enable you to invest as little as $5 into a range of ETFs and index funds.
Remember, investing is a long-term game. It’s essential to be patient, disciplined, and informed. By starting early, being consistent, and staying informed, you can achieve your financial goals and build a secure financial future.
Key Takeaways
In conclusion, starting your investment journey requires a solid understanding of the fundamentals, a clear investment plan, and a long-term perspective. By avoiding common mistakes, such as investing without a strategy or failing to diversify, you can set yourself up for success. Remember to assess your risk tolerance, evaluate your investment options, and create a well-diversified portfolio that aligns with your financial goals.
As you begin your investment journey, ask yourself: what are your financial goals, and what steps can you take today to start achieving them? By taking control of your finances, educating yourself, and staying committed to your goals, you can build a secure financial future and achieve long-term success. So, take the first step, and start investing in your future today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best way to start investing?
Start by setting financial goals and creating a personalized investment plan
How much money do I need to start investing?
You can start investing with a small amount of money, even $100
What are the risks of investing?
There are risks associated with investing, but you can manage them by diversifying your portfolio and having a long-term perspective