The landscape of web development shifts constantly. What was cutting-edge three years ago might now be outdated, while technologies that barely existed are now industry standards. For businesses seeking web development in Sri Lanka, understanding the current state of technology matters—not because you need to become a developer yourself, but because informed clients make better decisions and get better results.
This overview examines what’s happening in web development as we move through 2026, with particular attention to how Sri Lankan developers are adopting and adapting these technologies for local market needs.
Frontend Frameworks: Where the User Experience Lives
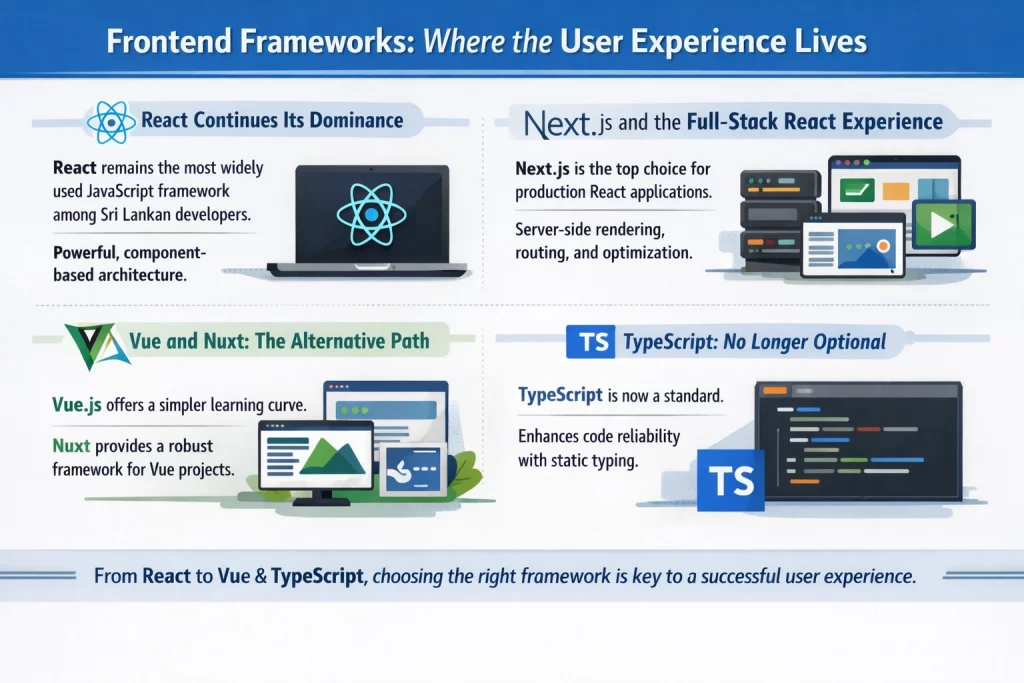
The frontend—everything users see and interact with directly—has seen remarkable evolution. Gone are the days when websites were simply collections of static pages. Modern frontends behave more like applications, responding instantly to user actions and providing experiences that rival native mobile apps.
React Continues Its Dominance
React, developed by Meta, remains the most widely used JavaScript framework among Sri Lankan developers. Its component-based architecture allows developers to build complex interfaces from reusable pieces, improving both development efficiency and code maintainability.
For businesses, React’s dominance means a large talent pool. Finding developers who know React is easier than finding specialists in less common frameworks. This affects not just initial development but long-term maintenance—you want your site built with technology that others can work on if your original developer becomes unavailable.
Recent additions to the React ecosystem, particularly Server Components and improved streaming capabilities, have addressed earlier criticisms about performance and SEO friendliness. Sites built with modern React can achieve excellent search engine visibility and blazing fast load times when properly implemented.
Next.js and the Full-Stack React Experience
Next.js has become the go-to framework for building production React applications. It handles the complex infrastructure decisions that would otherwise require significant expertise—server-side rendering, code splitting, image optimization, routing—allowing developers to focus on building features rather than wrestling with configuration.
Sri Lankan web development companies increasingly default to Next.js for client projects requiring custom functionality. It strikes an appealing balance between power and productivity, enabling sophisticated applications without excessive development time.
Vue and Nuxt: The Alternative Path
Vue.js offers a gentler learning curve than React while achieving similar results. Some Sri Lankan teams prefer Vue for projects where they need to bring junior developers up to speed quickly or where the project doesn’t justify React’s additional complexity.
Nuxt serves Vue the way Next.js serves React—providing a production-ready framework with sensible defaults. For content-heavy sites where Vue’s simplicity is appealing, Nuxt represents an excellent choice.
TypeScript: No Longer Optional
TypeScript has transitioned from a nice-to-have to a standard expectation. By adding type safety to JavaScript, TypeScript catches errors during development rather than in production, significantly improving code reliability.
When evaluating developers, asking about TypeScript usage tells you something about their approach to quality. Teams working in TypeScript are generally writing more maintainable, less error-prone code.
Backend Technologies: The Engine Room

While users never see backend code directly, it powers everything—handling data, processing transactions, managing authentication, connecting to external services. Backend choices affect performance, security, and what’s possible to build.
Node.js Ecosystem
Node.js allows developers to use JavaScript on the server, creating unified development stacks where frontend and backend share a language. This has practical benefits: easier code sharing between layers, simpler team structures, and developers who can work across the full stack.
Express.js remains popular for Node.js APIs, though newer options like Fastify offer better performance for high-traffic applications. For more structured needs, NestJS provides an enterprise-grade framework with opinions about architecture and organisation.
PHP: Still Going Strong
Despite predictions of its decline, PHP powers a remarkable portion of the web—particularly through WordPress and other content management systems. Modern PHP (version 8 and beyond) has evolved significantly from its earlier iterations, with improved performance, better type support, and more elegant syntax.
For many Sri Lankan businesses, PHP-based solutions remain practical choices. The technology is mature, developers are abundant, hosting is straightforward and affordable, and frameworks like Laravel provide modern development experiences.
Python and Django
Python’s popularity in data science and machine learning has spilled over into web development. Django, Python’s main web framework, excels for applications requiring sophisticated data handling or integration with analytical capabilities.
If your project involves significant data processing, reporting, or potential machine learning features, a Python-based backend might position you well for future development.
Database Technologies: Managing Your Data
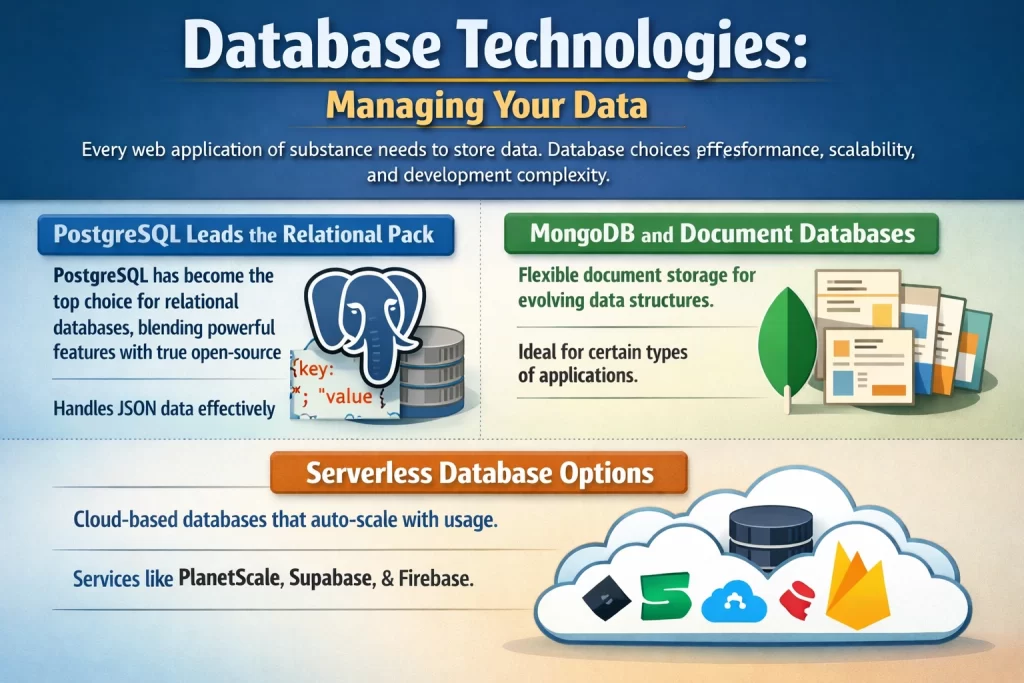
Every web application of substance needs to store data. Database choices affect performance, scalability, and development complexity.
PostgreSQL Leads the Relational Pack
PostgreSQL has emerged as the preferred choice for relational database needs. Its combination of robust features, excellent performance, and true open-source status has won over developers who previously defaulted to MySQL.
Modern PostgreSQL handles JSON data effectively, blurring traditional distinctions between relational and document databases. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of application types.
MongoDB and Document Databases
For applications with flexible, evolving data structures, document databases like MongoDB offer advantages. Rather than fitting data into predefined table structures, you can store documents with varying shapes—useful for certain types of applications.
However, the initial enthusiasm for NoSQL databases has tempered. Many developers have learned that traditional relational databases handle most use cases better, with document stores reserved for specific scenarios where their flexibility genuinely helps.
Serverless Database Options
Cloud providers now offer database services that scale automatically and charge based on usage—services like PlanetScale, Supabase, and Firebase. For applications with unpredictable traffic patterns or startups wanting to avoid infrastructure management, these options are compelling.
Deployment and Infrastructure
How websites get from developer machines to user browsers has transformed dramatically. Modern deployment approaches emphasise automation, reliability, and performance.
Containerisation with Docker
Docker allows applications to be packaged with all their dependencies, ensuring they run identically regardless of where they’re deployed. This eliminates the classic “it works on my machine” problem and simplifies deployment processes.
For complex applications, Kubernetes orchestrates containers at scale, managing deployment, scaling, and maintenance automatically. While overkill for smaller projects, Kubernetes expertise has become valuable for enterprise-grade applications.
Cloud Platforms and Edge Computing
AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure provide virtually unlimited infrastructure on demand. Sri Lankan web design in Sri Lanka increasingly leverages these platforms for reliability and global reach.
Edge computing—running code closer to users geographically—has become practical through services like Cloudflare Workers and Vercel Edge Functions. For sites serving international audiences, edge deployment can dramatically improve perceived performance.
Continuous Integration and Deployment
Modern development practices emphasise automation. Changes flow through testing and deployment pipelines without manual intervention, catching errors early and enabling rapid iteration. Tools like GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and CircleCI have made these practices accessible even for smaller teams.
Performance and Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals have made performance a ranking factor, giving businesses direct SEO incentive to prioritise speed. The metrics focus on real user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How quickly the main content appears
- First Input Delay (FID) and Interaction to Next Paint (INP): How responsive the page is to user interaction
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How stable the page is as it loads
Achieving good scores requires attention throughout development—efficient code, optimised images, strategic loading of resources, and stable layouts. These concerns should be part of project planning, not afterthoughts.
Security: Non-Negotiable in 2026
Security threats have grown more sophisticated, and the consequences of breaches more severe. Modern development incorporates security at every layer.
HTTPS Everywhere
SSL certificates are no longer optional—they’re baseline expectations. Browsers flag non-HTTPS sites as insecure, and search engines penalise them. Any reputable developer includes proper SSL configuration as standard practice.
Authentication and Authorisation
Managing user identity securely has become complex enough that most projects use dedicated services—Auth0, Firebase Auth, or similar. These handle the intricate security requirements of modern authentication, including multi-factor options, OAuth integration, and password security.
Input Validation and Sanitisation
SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and similar attacks remain threats. Modern frameworks include protections against common attacks, but developers must still follow secure coding practices. When evaluating development partners, asking about their security practices reveals much about their professionalism.
Accessibility: Building for Everyone

Web accessibility—ensuring sites work for users with disabilities—has gained both ethical recognition and legal significance. Modern development includes accessibility considerations from the start: semantic HTML, keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and sufficient colour contrast.
Beyond the ethical imperative, accessibility correlates with better SEO and improved usability for all users. Mobile users in bright sunlight benefit from good contrast. Users with slow connections benefit from sites that work without JavaScript. The accommodations made for accessibility often improve the experience universally.
What This Means for Your Project
Technology choices should serve business objectives, not exist for their own sake. Here’s how to apply this knowledge:
When evaluating web design companies in Sri Lanka, ask about their technology choices. They should be able to explain why they use specific frameworks and tools, relating those choices to your project needs. Beware of developers who seem stuck on outdated technologies or those who chase trends without clear rationale.
Don’t assume the newest technology is best for your project. Sometimes mature, established tools serve better than cutting-edge alternatives. A WordPress site might genuinely be the right choice even though it’s not the latest thing.
Prioritise performance and security regardless of technology stack. These aren’t features to add later—they need to be foundational. Ask prospective developers how they ensure both.
Consider long-term maintenance from the start. The technologies used affect how easily the site can be updated, who can work on it, and what future changes are possible.
The Sri Lankan Context
Local factors influence technology choices. Internet speeds, while improving, still vary significantly across Sri Lanka. Mobile dominates access. These realities should shape development decisions—prioritising performance, ensuring mobile excellence, and accounting for variable connection quality.
Local payment integration requirements mean understanding Sri Lankan banking systems and payment gateways. Local language support requires proper handling of Sinhala and Tamil scripts. These aren’t exotic requirements—they’re basic necessities for sites serving the Sri Lankan market.
The best web development partners combine global technology knowledge with local market understanding. They know what the international development community is doing and how to apply those practices effectively for Sri Lankan businesses and their customers.